
All Engineering Assessments
Assessment ABE-1-6A
Assist with fuel oil transfer
Assessed in EN-1211 Auxiliary Machinery I
Condition
On board ship or in laboratory
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
The candidate will:
|
Transfer is completed without incident All MARPOL/USCG recommendations for proper bunker procedures are followed No safety violations are observed. |
Supports Table A-III/5 able seafarer engine
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Contribute to fueling and oil transfer operations |
E-A6.1 Knowledge of the function and operation of fuel system and oil transfer operations, including:
|
Assist with fuel oil transfer |

Assessment OICEW-1-1A
Cut a circular hole using oxyacetylene process
Assessed in EN-2112 Machine Tool Technology
Condition
In a workshop/laboratory or other safe working environment, given proper tools, lighting, ventilation, and a thin steel plate of no less than 1/4 inch thickness.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Use Tools to cut a circular hole using oxy-fuel process |
Observe all personal and environmental safety procedures Light and adjust torch for cutting flame Hole radius is within ±1/8" of specifications |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Appropriate use of hand tools, machine tools and measuring instruments for fabrication and repair on board |
C1.6 Use of hand tools, machine tools and measuring instruments |
Cut a circular hole using oxyacetylene process |

Assessment OICEW-1-1B
Form two steel plates using brazing process
Assessed in EN-2112 Machine Tool Technology
Condition
In a workshop/laboratory or other safe working environment, given proper tools, lighting, ventilation, and two steel plates of no less than 1/8 inch thickness.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Use Tools to perform brazing process |
Observe all personal and environmental safety procedures Select brazing material, flux, and tip size appropriate for the job Prepare and clean plates Adjust torch for neutral flame Preheat plates Braze according to standard brazing procedure |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Appropriate use of hand tools, machine tools and measuring instruments for fabrication and repair on board |
C1.6 Use of hand tools, machine tools and measuring instruments |
Form two steel plates using brazing process |

Assessment OICEW-1-1C
Form two steel plates using electric arc welding process
Assessed in EN-2112 Machine Tool Technology
Condition
In a workshop/laboratory or other safe working environment, given proper tools, lighting, ventilation, and two steel plates of no less than 3/8 inch thickness.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Use Tools to fuse two steel plates using electric arc welding process |
Observe all personal and environmental safety procedures adjust welding machine settings as appropriate for the job Weld according to standard welding procedure |
|
Inspect resulting weld |
Identify any evidence of lack of fill, flux entrapment, non-continuous fillet, base metal erosion, base cracks or other defects |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Appropriate use of hand tools, machine tools and measuring instruments for fabrication and repair on board |
C1.6 Use of hand tools, machine tools and measuring instruments |
Form two steel plates using electric arc welding process |

Assessment OICEW-1-1D
Sweat joint
Assessed in ST-0999E Sea Term I (Engineering Portion)
Condition
In a workshop/laboratory or other safe working environment, given proper tools, lighting, ventilation, and 1/2 inch copper tube and coupling.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Plan fabrication of sweat joint fitting | |
|
Use:
Prepare joint by cleaning and fluxing | |
|
Test joint for tightness |
Prove joint leak free |
Attachment:
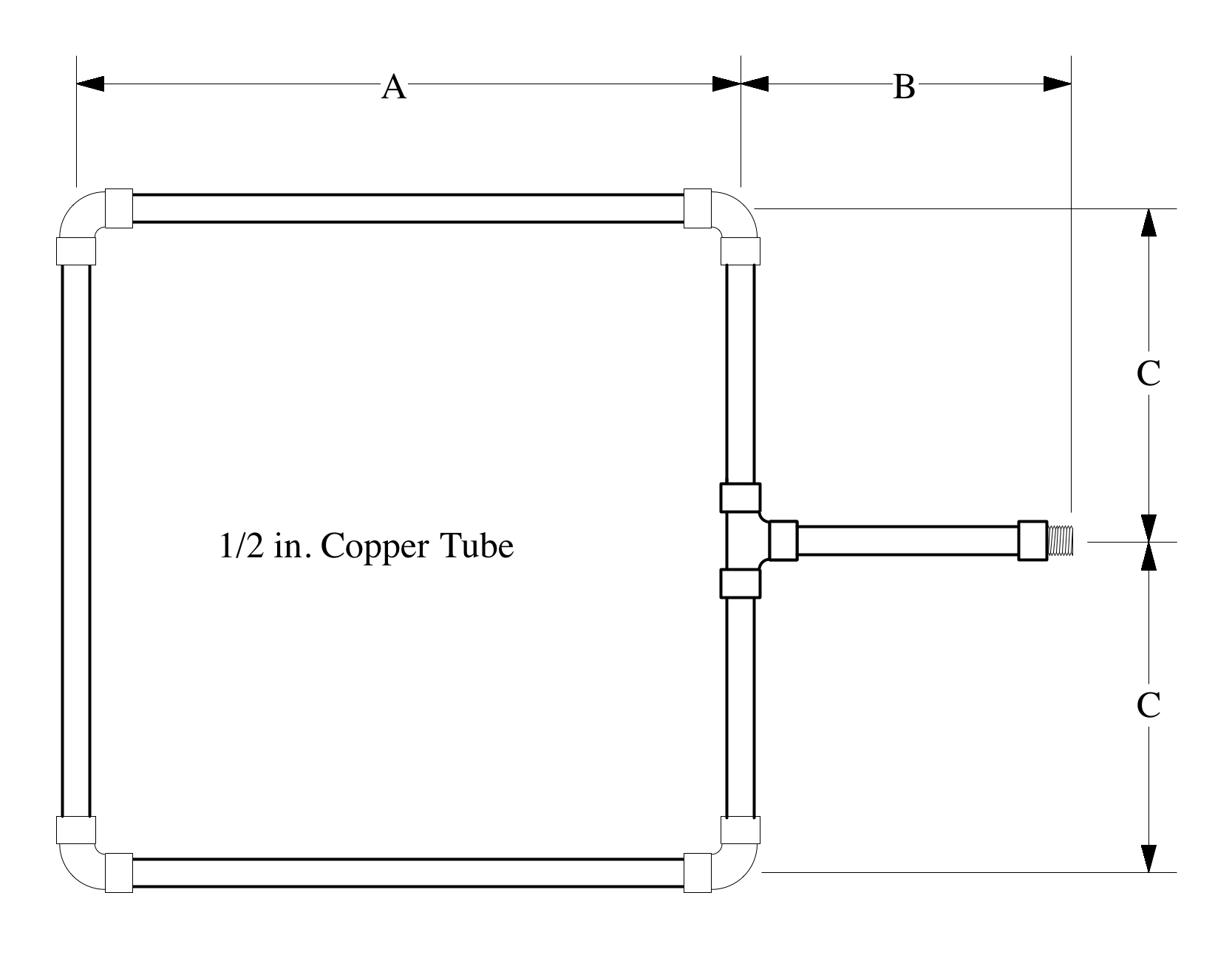
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Appropriate use of hand tools, machine tools and measuring instruments for fabrication and repair on board |
C1.6 Use of hand tools, machine tools and measuring instruments |
Sweat joint |

Assessment OICEW-1-1E
Bend copper tube
Assessed in ST-0999E Sea Term I (Engineering Portion)
Job Specifications
Cut and bend a 10" long section of 3/8" diameter copper tube to a 90° angle. Length should be within +/- 1/8" and bend should be free of defects and kinks and within angular tolerance of +/- 2°.
Condition
In a workshop/ laboratory or other safe working environment, given 3/8 inch copper tube of at least 10 inches long, proper tools, and lighting.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Plan to bend a copper tube to meet job specifications | |
|
Use tools to bend a tube to meet job specifications |
Use:
|
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Appropriate use of hand tools, machine tools and measuring instruments for fabrication and repair on board |
C1.6 Use of hand tools, machine tools and measuring instruments |
Bend copper tube |

Assessment OICEW-1-1F
Visual test of welded joint
Assessed in EN-2112 Machine Tool Technology
Condition
In a workshop/laboratory or other safe working environment, given proper tools and supplies.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Check a welded joint visually |
Prepare weld for visual inspection Identify any weld defects as described by American Welding Society, such as:
|
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Appropriate use of hand tools, machine tools and measuring instruments for fabrication and repair on board |
C1.2 Characteristics and limitations of processes used for fabrication and repair |
Visual test of welded joint |

Assessment OICEW-1-1G
Dye-penetrant test of welded joint
Assessed in EN-2112 Machine Tool Technology
Job Specifications
Test shall be conducted in accordance with ASTM Standard E1417 Visible Dye Penetrant Procedure (Type II Method C) or equivalent.
- Specimens should be visually examined for flaws before the application of penetrant.
- Specimens should be cleaned to remove contaminates that could prevent penetrant from entering discontinuities and thoroughly dried.
- Apply a thin, even coating of penetrant to the part by spraying.
- Allow the penetrant to dwell on the surface for 10 minutes or longer.
- Remove excess surface penetrant by wiping the surface with a dry lint-free cloth. Try to minimize the number of times the surface is wiped as each pass of the cloth could pull penetrant from a flaw.
- Finish the cleaning by dampening a cloth by spraying with solvent and wiping the surface one final time.
- Apply a light uniform coating of well agitated, non-aqueous wet developer by spraying. Excess developer will reduce the sensitivity of the inspection; this is the most common error made with liquid penetrants.
- Inspect the surface as the developer works to pull the penetrant from any surface breaking flaws to produce an indication. Allow the sample to develop for a minimum of 10 minutes.
- Record the location, size, orientation and other features of interest of any indications produced by the inspection.
- Clean all specimens by rinsing off the developer.
Condition
In a workshop/laboratory or other safe working environment, given proper tools and supplies.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Apply liquid penetrant and developer |
Apply penetrant and developer according to specifications |
|
Inspect prepared test coupon |
Identify visible defects such as:
|
Attachment:
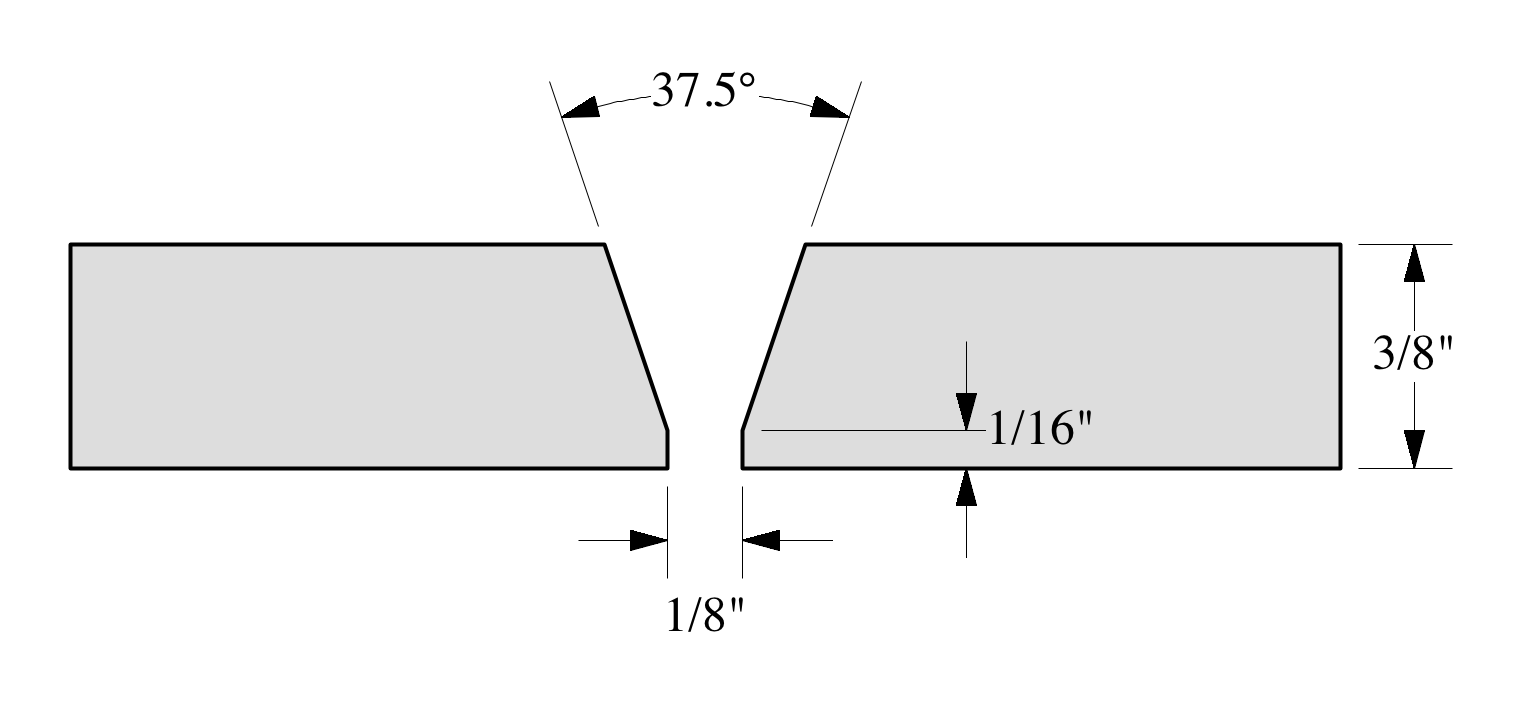
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Appropriate use of hand tools, machine tools and measuring instruments for fabrication and repair on board |
C1.2 Characteristics and limitations of processes used for fabrication and repair |
Dye-penetrant test of welded joint |

Assessment OICEW-2-1A
Drill blind hole using drilling machine
Assessed in ST-0999E Sea Term I (Engineering Portion)
Condition
In a workshop/laboratory or other safe working environment, given a drilling machine, proper tools, lighting, ventilation, and metal stock of no less than 1- inch thickness.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Use:
|
Attachment:
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Appropriate use of hand tools, machine tools and measuring instruments for fabrication and repair on board |
C1.6 Use of hand tools, machine tools and measuring instruments |
Drill blind hole using drilling machine |

Assessment OICEW-2-1B
Thread a blind hole using hand taps
Assessed in ST-0999E Sea Term I (Engineering Portion)
Condition
In a workshop/laboratory or other safe working environment, given a drilling machine, proper tools, lighting, ventilation, and metal stock of no less than 1- inch thickness, with a 3/8 inch diameter blind hole perpendicular to the surface.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Use:
|
Attachment:
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Appropriate use of hand tools, machine tools and measuring instruments for fabrication and repair on board |
C1.6 Use of hand tools, machine tools and measuring instruments |
Thread a blind hole using hand taps |

Assessment OICEW-2-1C
External thread using a hand die
Assessed in ST-0999E Sea Term I (Engineering Portion)
Condition
In a workshop/laboratory or other safe working environment, given a hand die, proper tools, lighting, ventilation, and steel round stock or pipe of no less than 3/8 inch diameter.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Plan to make an external thread on 1/2" pipe | |
|
Use tools to Fabricate an external thread on the 1/2" pipe with the axis of the pipe and thread co-linear |
Use:
|
Attachment:

Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Appropriate use of hand tools, machine tools and measuring instruments for fabrication and repair on board |
C1.6 Use of hand tools, machine tools and measuring instruments |
External thread using a hand die |

Assessment OICEW-3-1A
Plan and use test equipment
Assessed in EN-3111L Electrical Machines Lab
Condition
Given a voltmeter, ammeter, ohmmeter, simple circuit with a power source, and a schematic of the circuit with at least 5 components indicated.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Describe the use of electrical measuring equipment |
Indicate safety precautions Describe how to perform:
|
|
Test electrical circuits or components using electrical measuring equipment |
Do at least three of the following:
|
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Maintenance and repair of electrical and electronic equipment |
B2.4 Construction and operation of electrical testing and measuring equipment |
Plan and use test equipment |

Assessment OICEW-3-1B
Troubleshoot electrical motor control system
Assessed in EN-3111L Electrical Machines Lab
Condition
Aboard ship, in a workshop, or using a appropriate simulator, given the schematic of and access to the electrical control system, proper tools and safety equipment.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Inspect circuit |
Test system operation Note symptoms of faulty operation |
|
Identify possible causes of observed symptoms | |
|
Test controller circuits to locate faults |
Use meters to systematically discover cause of fault |
|
Repair system to clear fault and restore normal operation |
Identify and replace faulty component Complete all operations safely and within time limit and efficiently to receive credit for fault |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Maintenance and repair of electrical and electronic equipment |
B2.3 Detection of electric malfunction, location of faults and measures to prevent damage |
Troubleshoot electrical motor control system |

Assessment OICEW-3-1C
Detect location of grounds
Assessed in EN-4231 Sea Term IV: Marine Engineering
Condition
Aboard ship, in a workshop, or using an approved simulator, given access to an electrical distribution system, and proper tools and safety equipment.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Describe operation of ground fault detection systems |
Define a ground fault State common causes of ground faults State behavior of ground lamps |
|
Operate ground fault simulator |
Introduce ground fault and observe behavior of ground lamps Introduce a second ground fault, and observe behavior of circuit breaker |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Maintenance and repair of electrical and electronic equipment |
B2.3 Detection of electric malfunction, location of faults and measures to prevent damage |
Detect location of grounds |

Assessment OICEW-3-1D
Measure insulation resistance
Assessed in EN-4231 Sea Term IV: Marine Engineering
Condition
Aboard ship or in a workshop, given access to 3-phase electrical AC motor and controller, a Megger test meter, and other proper tools and safety equipment.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Measure motor insulation resistance at motor controller |
Use megger to perform insulation spot test:
|
|
Correct insulation resistance measurement to standard temperature. |
Correct reading to 40 °C using nomograph or correction chart. |
|
Evaluate insulation resistance value |
Compare corrected resistance to IEEE standard. State whether resistance value is within acceptable limits |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Maintenance and repair of electrical and electronic equipment |
B2.3 Detection of electric malfunction, location of faults and measures to prevent damage |
Measure insulation resistance |

Assessment OICEW-3-1E
Determine phase rotation
Assessed in EN-4231 Sea Term IV: Marine Engineering
Condition
Aboard ship or in a workshop, given access to 3-phase electrical AC motor controller, a phase sequence indicator, and other proper tools and safety equipment.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Check phase rotation using phase rotation meter prior starting an ac motor |
Use meter according to manufacturers instructions Identify phase sequence on meter Match phase sequence to motor rotation direction |
|
Determine if phase rotation is correct for desired direction of motor rotation |
Predict direction motor will rotate Verify motor rotates in predicted direction State how to reverse motor |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Maintenance and repair of electrical and electronic equipment |
B2.4 Construction and operation of electrical testing and measuring equipment |
Determine phase rotation |

Assessment OICEW-4-1A
Inspect machinery spaces before assuming watch
Assessed in EN-4231 Sea Term IV: Marine Engineering
Condition
Aboard ship, having a main propulsion machinery of 750 kW or more, while underway in engine room.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Check uptakes |
check:
|
|
Check steering gear |
Check:
|
|
Check shaft alley |
Check:
|
|
Check operating pumps and essential stand by units |
Check:
|
|
Check engine room bilges |
Check:
|
|
Check fire room |
Determine mode of boiler operation Determine the status of automated controls, including:
Check status of stand-by units |
|
Check main and auxiliary condensers |
Check:
Determine line-up of:
|
|
Check fresh water system |
Check:
|
|
Check control console status |
Check:
|
|
Check main engine |
Check:
|
|
Check electrical generation |
Check:
|
|
Check refrigeration equipment |
Check:
|
|
Check fuel and water tanks |
Check:
|
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Maintain a safe engineering watch |
A1.1 Thorough knowledge of Principles to be observed in keeping an engineering watch, including:
|
Inspect machinery spaces before assuming watch |

Assessment OICEW-4-1B
Watch Relief
Assessed in EN-4231 Sea Term IV: Marine Engineering
Pre-watch debrief
Prior to taking over the engineering watch, relieving officers shall satisfy themselves regarding at least the following:
|
The standing orders and special instructions of the chief engineer officer relating to the operation of the ship's systems and machinery; |
|
|
The nature of all work being performed on machinery and systems, the personnel involved and potential hazards; |
|
|
The level and, where applicable, the condition of water or residues in bilges, ballast tanks slop tanks, reserve tanks, fresh water tanks, sewage tanks and any special requirements for use or disposal of the contents thereof; |
|
|
The condition and level of fuel in the reserve tanks, settling tank, day tank, and other storage facilities; |
|
|
Any special requirements relating to sanitary system disposals; |
|
|
Condition and mode of operation of the various main and auxiliary systems, including the electrical distribution system; |
|
|
Where, applicable, the condition of monitoring and control console equipment, and which equipment is being operated manually; |
|
|
Where applicable, the condition and mode of operation of automatic boiler controls such as flame safeguard control systems, limit control systems, combustion control systems, fuel-supply control systems and other equipment related to the operation of steam boilers; |
|
|
Any potentially adverse conditions resulting from bad weather, ice, or contaminated shallow water; |
|
|
Any special modes of operation dictated by equipment failure or adverse ship conditions; |
Is any machinery or controls out of service or in hand mode? Is there anything unusual about this watch? |
|
The reports of engine-room ratings relating to their assigned duties; |
|
|
The availability of fire-fighting appliances; and |
|
|
The state of completion of the engine-room log. |
|
Condition
Aboard ship while underway, or in an approved simulator, given the engineering log book, the pertinent standing orders and proper safety equipment.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Check engine room and machinery in accordance with stcw code (a-vii/2 part 3-2 §58) |
|
|
Check that all members of the relieving watch are ready to perform their duties |
Insure:
|
|
Relieve the watch |
Clearly indicate when watchstanding responsibility is assumed |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Maintain a safe engineering watch |
A1.1 Thorough knowledge of Principles to be observed in keeping an engineering watch, including:
|
Watch Relief |

Assessment OICEW-4-2A
Respond to engine room alarms
Assessed in EN-3233 Steam and Gas Turbines
Condition
Aboard ship or in a suitable engine room simulator, given appropriate alarms.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Monitor the simulated plant | |
|
Respond to alarms |
For each alarm that occurs:
|
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Maintain a safe engineering watch |
A1.3 Safety precautions to be observed during a watch and immediate actions to be taken in the event of fire or accident, with particular reference to oil systems |
Respond to engine room alarms |

Assessment OICEW-4-3B
Prepare and start main gas turbine
Assessed in EN-3233 Steam and Gas Turbines
Condition
On a gas-turbine vessel of at least 1,000 HP at sea, on a simulator, or in a laboratory
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Check for sufficient electrical capacity |
|
|
Prepare main gas turbine for start |
|
|
Start main gas turbine engines |
|
Supports Table
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Operate main and auxiliary machinery and associated control systems |
A4.3 Preparation, operation, fault detection and necessary measures to prevent damage for the following machinery items and control systems:
|
Prepare and start main gas turbine |

Assessment OICEW-4-3E
Monitor main gas turbine operation
Assessed in EN-3233 Steam and Gas Turbines
Condition
On a gas-turbine vessel of at least 1,000 HP at sea, on a simulator, or in a laboratory.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Shift controls |
shift/change over controls from local or main control room to bridge control |
|
Adjust engine speed as required |
adjust throttles to match engine order telegraph (EOT) |
|
Monitor main gas turbine engine |
|
|
Monitor gas turbine alarms |
respond to alarms and take corrective actions as necessary |
Supports Table
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Operate main and auxiliary machinery and associated control systems |
A4.3 Preparation, operation, fault detection and necessary measures to prevent damage for the following machinery items and control systems:
|
Monitor main gas turbine operation |

Assessment OICEW-4-3H
Secure main gas turbine
Assessed in EN-3233 Steam and Gas Turbines
Condition
On a gas-turbine vessel of at least 1,000 HP at sea, on a simulator, or in a laboratory
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Prepare to secure main gas turbine |
|
|
Secure main gas turbine engines |
|
|
Monitor alarms |
Respond to alarms and take corrective actions as necessary |
Supports Table
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Operate main and auxiliary machinery and associated control systems |
A4.3 Preparation, operation, fault detection and necessary measures to prevent damage for the following machinery items and control systems:
|
Secure main gas turbine |

Assessment OICEW-5-1A
Steering gear test
Assessed in EN-4231 Sea Term IV: Marine Engineering
Condition
Aboard ship at steering room station or in an approved simulator.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Check steering gear is ready for operation |
Check:
|
|
Establish communications with bridge |
Use sound powered phone. Use correct procedures and terminology |
|
Insure that the steering engine and the rudder are synchronized in the midship position before starting or stopping pumps Have bridge operate each main steering engine assembly through full range of travel in normal mode and nfu mode Transfer control to local and test trick wheel mode Verify operation of rudder angle indicator system with bridge Note rudder travel time from stop to stop Note any unusual operation, noises or leakage | |
|
Check alternate power sources |
Verify that normal and emergency power feeders are functional |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Operate main and auxiliary machinery and associated control systems |
A4.1 Basic construction and operation principles of machinery systems, including:
|
Steering gear test |

Assessment OICEW-5-1B
Start refrigeration system
Assessed in EN-3213 Refrigeration
Note: Not all steps are possible on all refrigeration systems.
Condition
Using an approved simulator, in the laboratory, or aboard ship and given access to a refrigeration system that has been secured.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Identify the valves and equipment associated with the refrigeration unit |
Identify:
|
|
Check compressor lubrication |
Verify visible oil level |
|
Check refrigerant level |
Verify visible receiver level |
|
Line-up refrigeration unit |
Line up cooling water supply LIne up refrigerant circuit Leave compressor suction valve closed |
|
Start associated equipment |
Energize box solenoids Start diffuser fans, brine pumps, etc. as required |
|
Start the refrigeration compressor |
Gradually open compressor suction valve Verify:
|
|
Operate the refrigeration unit until conditions stabilize |
Monitor:
|
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Operate main and auxiliary machinery and associated control systems |
A4.1 Basic construction and operation principles of machinery systems, including:
|
Start refrigeration system |

Assessment OICEW-5-1C
Shut down refrigeration system
Assessed in EN-3213 Refrigeration
Note: Not all steps are possible on all refrigeration systems.
Condition
Using an approved simulator, in the laboratory, or aboard ship and given access to an operating refrigeration system.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Secure the refrigerant circuit |
Close the receiver outlet valve Pump down the receiver Observe suction pressure |
|
Secure the refrigeration compressor |
Observe compressor stop on low pressure cut-out De-energize the compressor Close compressor suction and discharge valves |
|
Secure associated equipment |
Secure secondary refrigerant loop, if used Secure box solenoid, if shutting down |
|
Secure the cooling water supply |
Close valves and secure pumps as required |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Operate main and auxiliary machinery and associated control systems |
A4.1 Basic construction and operation principles of machinery systems, including:
|
Shut down refrigeration system |

Assessment OICEW-5-1D
Start air compressor
Assessed in EN-2111 Auxiliary Machinery II
Condition
Using an approved simulator, in the laboratory, or aboard ship and given access to an air compressor.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Check unit for readiness to start |
Inspect mechanical condition of equipment Observe sufficient lubricating oil Blow down receiver and moisture traps On water cooled units, verify coolant flow |
|
Line-up compressor |
Verify compressor discharge valve is open |
|
Start compressor |
press start button verify control set to automatic |
|
Monitor operation of air compressor |
Verify operation of unloader Verify operation of cut-in and cut-out switches |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Operate main and auxiliary machinery and associated control systems |
A4.1 Basic construction and operation principles of machinery systems, including:
|
Start air compressor |

Assessment OICEW-5-1E
Shut down air compressor
Assessed in EN-2111 Auxiliary Machinery II
Condition
Using an approved simulator, in the laboratory, or aboard ship and given access to an air compressor.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Secure the air compressor |
Press the stop button Leave compressor lined up to start |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Operate main and auxiliary machinery and associated control systems |
A4.1 Basic construction and operation principles of machinery systems, including:
|
Shut down air compressor |

Assessment OICEW-5-1F
Start fresh water generator
Assessed in EN-4231 Sea Term IV: Marine Engineering
Recommended Evaporator Start-up Procedure (TS Enterprise Specific)
Check that the following valves are open:
- Brine pump overboard
- Chemical feed pump discharge
- Feed heater attemporator supply
- Sea water heater vent to drain regulator
- Sea water heater drain to bilge
- Air ejector condensers drain to bilge
- Distillate pump sealing line
- Distillate pump discharge valve
- Distillate discharge to distribution manifold
- Inlet valve to reserve feed or potable tank
- Sea water suction valve to sea water supply
Check that the following valves are closed:
- Air ejector condenser drain to ADT
- Sea water feed heater drain to auxiliary condenser
- Sea water feed regulating valves to 1st effect/Brine pump discharge
Start:
- Sea water feed pump and throttle inlet to 1st effect
- Chemical feed pump (insure proper level in tank)
- Brine pump and maintain level in 2nd effect hotwell
Open:
- Steam supply to air ejectors
- Steam supply to feed heaters (auxiliary exhaust or L.P. bleed)
- Feed heat attemporator root valve from condensate system
Turn on:
Salinity panel (insure 3 way dump valve is tripped to bilge)
Monitor:
- Feed heater shell temperature between 185-205° F.
- Sea water feed temperature between 165-170° F.
Start:
Distillate pump, and regulate level by throttling discharge valve
Line up:
- 3-way trip valve to proper tanks when salinity is less than .25 gpg
- Secure air ejector condenser drain to bilge and direct drains to ADT
- Secure sea water feed heater drain to bilge and direct drains to the auxiliary condenser
Condition
Using an approved simulator, in the laboratory, or aboard ship and given access to a fresh water generator.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Identify the valves and pumps associated with the freshwater generator |
identify:
|
|
Start the freshwater generator |
follow the ship specific evaporator starting procedure provided during training |
|
Line up the discharge to meet operational requirements |
Before proceeding:
|
|
Operate the freshwater generator until operations stabilize |
Check:
|
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Operate main and auxiliary machinery and associated control systems |
A4.1 Basic construction and operation principles of machinery systems, including:
|
Start fresh water generator |

Assessment OICEW-5-1G
Shut down fresh water generator
Assessed in EN-4231 Sea Term IV: Marine Engineering
Condition
Using an approved simulator, in the laboratory, or aboard ship and given access to a fresh water generator.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Identify the valves and pumps associated with the freshwater generator |
Identify:
|
|
Line up distillate discharge to the bilge | |
|
Secure the freshwater generator |
Follow the ship specific evaporator securing procedure provided during training |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Operate main and auxiliary machinery and associated control systems |
A4.1 Basic construction and operation principles of machinery systems, including:
|
Shut down fresh water generator |

Assessment OICEW-5-1H
Start fuel oil or lube oil purifier
Assessed in EN-3233 Steam and Gas Turbines
Condition
Using an approved simulator, in the laboratory, or aboard ship, given access to a fuel oil or lube oil purifier.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Identify the valves and equipment associated with the purifier unit |
Identify:
|
|
Line-up purifier unit |
Line up correct valves from suction to discharge |
|
Start the purifier |
Start prime mover and bring up to speed Secure if excessive vibration is noted Prime purifier Verify:
|
|
Monitor the purifier until conditions stabilize |
Monitor:
|
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Operate main and auxiliary machinery and associated control systems |
A4.1 Basic construction and operation principles of machinery systems, including:
|
Start fuel oil or lube oil purifier |

Assessment OICEW-5-1I
Shut down fuel oil or lube oil purifier
Assessed in EN-3233 Steam and Gas Turbines
Condition
Using an approved simulator, in the laboratory, or aboard ship, given access to a running fuel oil or lube oil purifier.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Secure the purifier oil heater | |
|
Secure purifier |
Close purifier suction valve Stop purifier motor Use bowl brake to bring bowl to stop |
|
Secure piping system |
Close discharge valve Close other valves as required |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Operate main and auxiliary machinery and associated control systems |
A4.1 Basic construction and operation principles of machinery systems, including:
|
Shut down fuel oil or lube oil purifier |

Assessment OICEW-5-1J
Prepare main propulsion diesel engine for operation
Assessed in EN-4131 Internal Combustion Engines II
Condition
In an approved simulator, in the laboratory, or aboard a ship and given access a main propulsion diesel engine.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Check:
| |
|
Check:
| |
|
Check:
| |
|
Line up and Start high temperature freshwater cooling system |
Check:
|
|
Check:
| |
|
Check:
| |
|
Check:
Select upper or lower tank based on draft | |
|
Start turning gear |
Prior to starting, check:
Obtain wheel clearance Start turning gear |
|
Bypass fuel oil meter while warming up Heat oil if necessary Viscosity control on auto Start fuel booster pump | |
|
Line up start air system |
Check pressure available Drain cooler and receiver Align system |
|
Secure turning gear |
Stop motor Disengage turning gear |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Operate main and auxiliary machinery and associated control systems |
A4.1 Basic construction and operation principles of machinery systems, including:
|
Prepare main propulsion diesel engine for operation |

Assessment OICEW-5-1K
Secure main propulsion diesel engine
Assessed in EN-4131 Internal Combustion Engines II
Condition
In an approved simulator, in the laboratory, or aboard a ship and given access a main propulsion diesel engine.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Secure fuel supply |
Receive permission from bridge Insure shaft is stopped |
|
Start turning gear |
Prior to starting, check:
Obtain wheel clearance Start turning gear |
|
Secure cooling systems |
Secure:
|
|
Secure turning gear |
Stop motor Disengage turning gear |
|
Secure Lubricating Systems |
Secure
|
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Operate main and auxiliary machinery and associated control systems |
A4.1 Basic construction and operation principles of machinery systems, including:
|
Secure main propulsion diesel engine |

Assessment OICEW-5-1L
Prepare main steam turbine for operation
Assessed in EN-4231 Sea Term IV: Marine Engineering
Recommended Turbine Start-up Procedure (TS Enterprise Specific)
Line up and Start Main Lube Oil System:
- Check that Lube Oil temperature is 90° F
- Check that alarm signal panel is energized
- Test low gravity tank alarm
- Test lube oil pump failure alarm
- Test low lube oil pressure alarm
- Line up selected lube oil cooler
- Line up motor driven lube oil pump
- Open lube oil fill/dump valve to lube oil gravity tank
- Start motor driven lube oil service pump
- Start lube oil standby pump in standby mode
- Insure lube oil pump failure alarm reading normal
- Insure lube oil gravity tank alarm is reading normal
- Insure lube oil low pressure alarm is reading normal
- Inspect all engine lube oil sight glasses to insure visual flow
- Verify lube oil flow in bull's eye
- Check that no leaks exist in the lube oil system
Place into Service Jacking Gear:
- Open all turbine casing drains
- Verify lubrication of bearings and gears
- Check all spring bearings and insure proper lube oil level
- Check stern tube packing gland for slight leakage and tightness
- Confirm no obstructions exist around propeller
- Request permission from bridge to start jacking gear
- Remove padlock and pin
- Rotate lever to engaged position
- Push pin through lever and replace padlock to secure pin
- Start jacking gear motor
- Place "Jacking Gear Engaged" sign on main throttles
- Record main engine thrust readings in engineroom log book
Line up and Start Main Circulating system:
- Open main condenser overboard valve
- Open suction valve to main circulating pump
- Start main circulating pump in low speed
- Vent main condenser heads
Line up and Start Main Condensate System:
- Open suction, vent, gage and sealing line to main condensate pump
- Open condensate recirculating valve one full turn
- Start the main condensate pump and open the discharge
- Monitor D.C. heater level and auxiliary exhaust pressure
Line up and Start Gland Seal System
- Open gland exhaust valve from engine to gland exhaust condenser
- Drain down and admit steam to glands using gland seal regulator bypass
- Place into service gland seal regulator and adjust to maintain 1/2 to 2 psig
Line up and Start Air Ejector and raise vacuum
- Select either port or starboard set of main air ejectors
- Open 1st and 2nd stage air ejector suction and discharge valves
- Admit steam to 2nd stage nozzle
- At 16-20 inches Hg apply steam to 1st stage nozzle
- Monitor air ejector steam pressure, adjust as necessary at regulator
Applying steam to the engine (placing into service):
Caution needs to be taken to insure gradual warmup of main steam lines and the throttle valve assembly. Prior to admitting steam to the throttle valve assembly fully open and lightly seat the ahead and astern throttle and inspect and linkage.
- One hour prior to receiving standby, warm up main steam line by opening bypasses on the main steam stop and bulkhead stop valves
- Open all throttle drains
- Receive permission from bridge to roll the engine
- Stop and disengage the Jacking Gear
- Remove "Jacking Gear Engaged" sign from throttles
- Align throttle drains to D.C. Heater
- Slowly open main steam and bulkhead stop valves
- Insure 19 nozzles configuration to HP turbine are open
- Open astern guarding valve
- Open astern throttle first and confirm engine rpms (No more than 10)
- Alternate ahead and astern throttle no more than 10 rpms
- Continue until steam line temperature to HP turbine is 500 degree F.
- Do not let hot rotor stand still for more than five minutes
- Insure all proper personnel are present for maneuvering
- Notify bridge that engineroom is ready to "answer all bells"
- Establish time of "stand-by engines" with bridge
- Close casing drains at first half-ahead bell
Condition
In an approved simulator or aboard a ship in port or at anchor, given access to a main steam turbine.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Verify stern tube and line shaft lube oil Verify minimum lube oil temperature Verify oil flow to all bearings Verify gravity tank overflow | |
|
Place into service jacking gear |
Check for propeller obstructions and obtain wheel clearance Hang jacking gear engaged sign |
|
Verify coolant flow | |
|
open main condensate pump vent and seal adjust main condensate recirculating valve monitor dc heater level | |
|
line up gland exhaust adjust gland seal regulator to 1.5 psig | |
|
Direct steam to second stage Raise vacuum to approximately 20 inches Hg |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Operate main and auxiliary machinery and associated control systems |
A4.1 Basic construction and operation principles of machinery systems, including:
|
Prepare main steam turbine for operation |

Assessment OICEW-5-1M
Monitor main steam turbine operation
Assessed in EN-2231 Sea Term II: Marine Engineering
Condition
In an approved simulator or aboard a ship underway, given access to a main steam turbine.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Identify turbine instrumentation available at console |
Identify these items:
|
|
Monitor turbine and reduction gears while underway |
Monitor for at least one hour Monitor these items:
|
|
Monitor turbine exhaust system |
Monitor these items:
|
|
Monitor the turbine lubrication system |
Monitor these items
|
|
Operate lube oil cooler |
Maintain temperature at 110° F. State normal operating temperature range State critical temperature limits (40° F rise or 160° F max.) |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Operate main and auxiliary machinery and associated control systems |
A4.1 Basic construction and operation principles of machinery systems, including:
|
Monitor main steam turbine operation |

Assessment OICEW-5-1N
Secure main steam turbine operation
Assessed in EN-4231 Sea Term IV: Marine Engineering
Condition
In an approved simulator or aboard a ship in port or at anchor, given access to a main steam turbine.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Secure steam to main engine |
Bleed pressure using throttles Monitor main steam line pressure Secure main and bulkhead stops and guardian valve |
|
Place into service jacking gear |
Hang jacking gear engaged sign |
|
Secure main air ejector and gland seal |
Insure MUF, exhaust dump, ADT, etc. are directed to auxiliary condenser Secure air ejector before gland seal |
|
Secure main condensate system |
Monitor hotwell and dc heater level |
|
Monitor main engine until cool |
Continue until LP casing temperature is about 150° F |
|
Secure main circ. system | |
|
Secure jacking gear |
Remove jacking gear engaged sign |
|
Secure main lube oil system |
Secure LO gravity tank |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Operate main and auxiliary machinery and associated control systems |
A4.1 Basic construction and operation principles of machinery systems, including:
|
Secure main steam turbine operation |

Assessment OICEW-5-2A
Light off main boiler
Assessed in EN-3233 Steam and Gas Turbines
Condition
In an approved simulator or aboard a ship in port or at anchor, given access to a main boiler.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Check and prepare boiler for light off |
Insure adequate water in drum Open:
|
|
Light off boiler |
Start force draft Open dampers and purge furnace Light fires Correctly proportion fuel/air ratio to prevent smoke |
|
Monitor boiler |
Monitor:
|
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Operate main and auxiliary machinery and associated control systems |
A4.1 Basic construction and operation principles of machinery systems, including:
|
Light off main boiler |

Assessment OICEW-5-2B
Secure main boiler
Assessed in EN-3233 Steam and Gas Turbines
Condition
In an approved simulator or aboard a ship in port or at anchor, given access to a main boiler.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Secure boiler |
Reduce load on boiler Place combustion control on manual Secure fires Open superheater vents and drains |
|
Secure forced draft fan | |
|
Monitor boiler until stabile |
Maintain water level in drum Open drum vent before pressure falls to 0 psi |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Operate main and auxiliary machinery and associated control systems |
A4.1 Basic construction and operation principles of machinery systems, including:
|
Secure main boiler |

Assessment OICEW-5-2C
Bottom blow boiler
Assessed in EN-3233 Steam and Gas Turbines
Condition
In an approved simulator or aboard a ship, given access to a main boiler.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Describe purpose of boiler blowdown | |
|
Blow down the boiler |
Raise water level to top of gage glass Open bottom blow valve When water level falls to bottom of glass, secure bottom blow valve |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Operate main and auxiliary machinery and associated control systems |
A4.1 Basic construction and operation principles of machinery systems, including:
|
Bottom blow boiler |

Assessment OICEW-5-2D
Boiler water test
Assessed in EN-3131 Steam Generators
Condition
In an approved simulator, laboratory, or aboard a ship, given access to a boiler water sample and test equipment.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Describe the purpose of boiler water testing |
Describes the consequences of failure to maintain boiler water quality |
|
Test the boiler water |
Conduct the following boiler water tests:
|
|
Evaluate the test results |
Compare results to operational limits Recommend corrective actions, if necessary |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Operate main and auxiliary machinery and associated control systems |
A4.3 Preparation, operation, fault detection and necessary measures to prevent damage for the following machinery items and control systems:
|
Boiler water test |

Assessment OICEW-5-3A
Check boiler water level
Assessed in EN-2231 Sea Term II: Marine Engineering
Condition
In an approved simulator or aboard a ship in port or at anchor, given access to a main or auxiliary boiler.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Describe means for determining boiler water level |
Describe all available means:
|
|
Describe the consequences of high and low water | |
|
Monitor boiler water level |
Monitor for a minimum of 1 hour |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Operate main and auxiliary machinery and associated control systems |
A4.3 Preparation, operation, fault detection and necessary measures to prevent damage for the following machinery items and control systems:
|
Check boiler water level |

Assessment OICEW-5-3B
Respond to boiler high water alarm
Assessed in EN-3233 Steam and Gas Turbines
Condition
In an approved simulator or aboard a ship in port or at anchor, given access to a main or auxiliary boiler.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Monitor the simulated plant | |
|
Respond to alarm |
Acknowledge the alarm Confirm alarm condition Assess cause of alarm condition Blow down boiler to decrease water level to safe value Correct situation by, as appropriate:
|
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Operate main and auxiliary machinery and associated control systems |
A4.3 Preparation, operation, fault detection and necessary measures to prevent damage for the following machinery items and control systems:
|
Respond to boiler high water alarm |

Assessment OICEW-5-3C
Respond to boiler low water alarm
Assessed in EN-3233 Steam and Gas Turbines
Condition
In an approved simulator or aboard a ship in port or at anchor, given access to a main or auxiliary boiler.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Monitor the simulated plant | |
|
Respond to alarms |
Acknowledge the alarm Confirm alarm condition Assess cause of alarm condition Correct situation by, as appropriate:
|
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Operate main and auxiliary machinery and associated control systems |
A4.3 Preparation, operation, fault detection and necessary measures to prevent damage for the following machinery items and control systems:
|
Respond to boiler low water alarm |

Assessment OICEW-6-1A
Transfer fuel
Assessed in EN-3233 Steam and Gas Turbines
Condition
Using an approved simulator or aboard ship, given proper fuel oil transfer procedures and equipment.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Plan a fuel transfer operation |
Identify source and destination tanks Estimate the:
|
|
Comply with all applicable regulations | |
|
Operate the transfer pump until the operational requirements have been met |
Monitor:
|
|
Secure the fuel oil transfer pump |
Stop pump Secure all valves |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Operate fuel, lubrication, ballast and other pumping systems and associated control systems |
A5.2 Operation of pumping systems:
|
Transfer fuel |

Assessment OICEW-6-1B
Operate fire pump
Assessed in EN-2231 Sea Term II: Marine Engineering
Condition
Using an approved simulator or aboard a ship, given piping diagram for the vessel and fire pump operating procedures.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Identify fire pumps and associated controls available in machinery spaces |
Identify three fire pumps Identify suction and discharge valves Identify control switches |
|
Line up to fire main Start with discharge valve closed | |
|
Monitor the fire pump |
Monitor discharge pressure |
|
Secure the fire pump |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Operate fuel, lubrication, ballast and other pumping systems and associated control systems |
A5.2 Operation of pumping systems:
|
Operate fire pump |

Assessment OICEW-6-2A
Operate bilge system
Assessed in EN-2231 Sea Term II: Marine Engineering
Condition
Aboard ship, or in an approved simulator, given the engineering log book, the pertinent standing orders, the oil record book, and proper safety equipment.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Plan a bilge pumping operation |
Identify space to be pumped Identify location to receive bilges Select bilge pump or ows to be used Insure sufficient room in slop tank, if used |
|
Comply with all applicable regulations | |
|
Operate the bilge pump or ows |
Monitor:
Maintain strainers as necessary |
|
Secure the bilge pump or OWS when pumping operation is complete |
Secure the bilge pump or OWS Secure the bilge manifold |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Operate fuel, lubrication, ballast and other pumping systems and associated control systems |
A5.2 Operation of pumping systems:
|
Operate bilge system |

Assessment OICEW-7-1A
Start emergency generator
Assessed in EN-4131 Internal Combustion Engines II
Condition
Aboard ship or in an approved simulator, given access to generator and proper tools.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Check that system is ready to start |
Meet requirements of OICEW 7-1B |
|
Start the generator |
Turn generator mode selector switch to manual Turn generator starting switch to start |
|
Check that generator starts properly |
Check:
|
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Operate electrical, electronic and control systems |
B1.1 Basic configuration and operation principles of the following electrical equipment:
|
Start emergency generator |

Assessment OICEW-7-1B
Pre-start inspection of diesel generator
Assessed in EN-4131 Internal Combustion Engines II
Condition
Aboard ship, in the laboratory, or in an approved simulator given access to proper equipment and manufacturer’s technical manual.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Check mechanical condition of engine |
Check:
|
|
Check engine lubrication |
Check dipstick for sufficient oil |
|
Check engine cooling |
Check expansion tank for sufficient water Check no obstructions blocking cooling fan |
|
Check engine fuel system |
Check level in fuel tank Verify alignment of fuel system |
|
Check engine starting system |
For hydraulic start:
For Electric start:
|
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Operate main and auxiliary machinery and associated control systems |
A4.1 Basic construction and operation principles of machinery systems, including:
|
Pre-start inspection of diesel generator |

Assessment OICEW-7-1C
Pre-start inspection of steam turbo-generator
Assessed in EN-3233 Steam and Gas Turbines
Recommended Turbogenerator Startup Procedure (T.S. Enterprise Specific)
Make preliminary checks
- Check the unit over for operational readiness i.e. no loose gear, all maintenance completed, strainers clean, manhole covers on, zincs intact, etc.
- Check the oil in the sump. The oil should be at the high mark on the dipstick, in good condition, uncontaminated with water or sludge, and at least 60° F, preferably higher. It can be cleaned and heated via the centrifugal purifier, if necessary.
- Ensure that the console operated pneumatic valve which controls steam to the generator throttle is closed, and that the generator circuit breaker is open.
Establish cooling water flow through the condenser
- Open the motorized auxiliary circulating pump high or low suction valve. Use the high suction in port.
- Open the motorized overboard discharge valve.
- Open the butterfly valve to condenser shell.
- Open the butterfly valve to the duplex strainer for the L.O. cooler and the generator air cooler.
- Start the auxiliary circulating pump. The discharge pressure should be 7-12 psig.
- Open the auxiliary circ. pump discharge globe valve. Starting a centrifugal pump before opening its discharge valve is good engineering practice, because it reduces the starting load on the drive motor; however, this practice is not always followed.
- Use the cooler inlet valves to restrict the cooling water flow to the generator LO cooler and air box cooler until they reach normal operating temperatures. (Normal: 110° F oil temperature at the LO cooler outlet, and 40° C generator air box temperature.
Establish cooling water flow through the auxiliary air ejector
Before the turbine is started and when it is operating under low loads, there is insufficient condensate to condense the air ejector steam. Condensate must be recirculated to supply sufficient coolant.
- Line up the condensate pump suction through the cone strainer, and discharge to the auxiliary air ejector condenser. (Three suction and two discharge valves on TSE).
- Open pump casing vent valves (Two on TSE).
- Open pump sealing water supply valve.
- Start the condensate pump, and open the condensate pump discharge valve.
- Open the recirc. regulator hand bypass valve from the outlet of the air ejector about one turn.
- Watch the level in the hotwell, and adjust the recirc flow to keep the level low in the sight glass. If the recirc valve is opened too wide, the hotwell will flood and the DC heater level will fall.
Start the Hydraulic Pressure Unit (HPU)
The Woodward speed control governor requires an external oil supply at a pressure of approximately 150 psig to operate the steam throttle valves. The HPUs are located on the lower level, starboard side.
- Check the sump oil level of the HPU for the SSTG to be started.
- Start either pump 1 or pump 2.
- Place the selector in auto, which will place the other pump in standby mode.
- Check the differential gage on the duplex discharge strainer when unit is running. One to two psig is normal.
Establish lubrication for turbine and reduction gears
There are thee separate lube oil pumps on the unit: a hand operated rotary pump, an attached IMO pump which is driven off the reduction gear, and a motor driven auxiliary oil pump. The turbogenerator sump holds 140 gallons of 2190-TEP oil. Additional oil can be added via the purifier, or by hand through the sump fill plug near the dipstick. The unit also has a duplex strainer that should be cleaned and changed daily.
- Start the auxiliary oil pump.
- Check pump discharge pressure: it should be about 90 psig. Oil pressure will open the steam throttle trip valve.
- Check oil pressure to the bearings: it should be 10-15 psig.
- Check bull's eyes for oil flow from all bearings.
Line up steam supply
The generators are supplied with superheated steam at 600 psi, 850°F through a manual turbogenerator steam stop at each boiler, and a manual stop valve and a console operated pneumatic valve at each generator. Steam lines should always be drained and warmed up before admitting steam to a turbine.
- Open the three steam traps on the turbogenerator.
- Open the steam stop valves at the generator.
- Open the generator stop valves at the port and/or starboard boiler.
- Open the drain before the control valve to the bilge slowly.
Raise vacuum
Note that each auxiliary air ejector is duplex: two complete sets of first and second stage ejector nozzles. Only one is normally used at a time.
- Line up vapor path: open first stage suction from condenser, second stage suction from intercondenser.
- Line up air ejector drains: Open inter condenser loop seal drain line to the auxiliary condenser. There is no valve in after condenser drain line to the atmospheric drain tank.
- Open 150 psi steam to the gland seal regulator and adjust it to 1.5 to 2.5 psig.
- Admit 150 psi steam to second stage air ejector nozzle. When the condenser vacuum reaches approximately 20 inches Hg, admit steam to the first stage. The vacuum should rise to 28-29 inches Hg.
- Adjust the recirc flow to maintain a condensate temperature of 90 to 125° F at the outlet from the air ejector condenser.
The turbine should be started spinning without delay after the vacuum is established to prevent the rotor from standing still in a hot environment, which would cause the rotor to bow and cause vibrations. Delaval recommends leaving the gland seal steam off until turbine is spinning to lessen the chance of rotor bowing.
Idle and warm up the turbine
On the console:
- Set voltage regulator control to OFF.
- Set IDLE-RATED selector to IDLE. This will set the speed governor set point to the idle speed of 2900 rpm.
- Set selector to RUN.
- Manually reset lube oil trip on front end of turbogenerator by pulling up on the round knob.
- Open pneumatically controlled steam valve using the pneumatic steam stop valve control knob located on the main console.
- Press the green start bypass button. The unit should start and run at approximately 2900 rpm.
Walk around the generator and check for any problems such as water or lube oil leaks, unusual noises, etc. If in doubt, shut the unit down.
Bring the turbine up to speed
- Allow the turbine to idle for about 30 minutes if possible, or at least until the oil temperature reaches 90°F. The generator should not be run above idle speed until the lube oil temperature reaches 90° F.
- Set IDLE-RATED selector switch to START. This sets the governor set point to the rated speed.
- Open the pneumatic valve fully: 71 psig air pressure. The turbine speed should rise and then stabilize at 10,012 rpm as the governor takes control.
- Set the voltage regulator control to AUTOMATIC.
Watch the unit carefully
- Keep your eye on the vacuum, oil pressure and temperature, air box temperature, and condensate temperature.
- Start cooling water to the lube oil cooler when the oil temperature comes up, and adjust to maintain 110° F.
- Adjust the cooling water flow to the air box to maintain 40° C.
- Adjust or secure recirc as necessary to maintain condensate temperature and hotwell level.
When you are satisfied with the operation of the turbo-generator, you can put it on the line.
Condition
Aboard ship, in the laboratory, or in an approved simulator given access to proper equipment and manufacturer’s technical manual.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Check for electrical readiness |
Look for:
|
|
Check system for operational readiness |
Look for:
|
|
Check for adequate lubrication |
Look for:
|
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Operate main and auxiliary machinery and associated control systems |
A4.1 Basic construction and operation principles of machinery systems, including:
|
Pre-start inspection of steam turbo-generator |

Assessment OICEW-7-1D
Connect ship service diesel generator to main switchboard
Assessed in EN-3233 Steam and Gas Turbines
Condition
Aboard a dead ship or in simulator, given access to generator and proper tools, approved instruction, and safe working environment.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Check that system is ready to start |
Meet requirements of OICEW 7-1B |
|
Start the generator |
Turn generator mode selector switch to manual Turn generator starting switch to start |
|
Check that generator starts properly |
Check:
|
|
Operate generator to achieve conditions suitable for synchronization |
Adjust generator to normal operating speed Place voltage regulator in manual Excite field Adjust frequency to 60 hz Adjust voltage to 120V |
|
synchronize incoming generator with bus |
Turn on synchroscope Match voltage and frequency with bus Close main breaker when generators are in phase Turn off synchroscope |
|
Adjust load on incoming generator |
Transfer voltage regulator to automatic Balance active (kw) load Balance reactive (kvar) load |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Operate electrical, electronic and control systems |
B1.1 Basic configuration and operation principles of the following electrical equipment:
|
Connect ship service diesel generator to main switchboard |

Assessment OICEW-7-1E
Parallel generators
Assessed in EN-3111L Electrical Machines Lab
Condition
Aboard ship, in the laboratory, or in an approved simulator given access to proper equipment and manufacturer technical manual.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Start incoming generator and raise voltage |
Start prime mover and bring up to operating speed Place voltage regulator in manual Excite field Adjust frequency to 60 hz Adjust voltage to system line voltage |
|
Synchronize incoming generator with bus |
Turn on synchroscope Match voltage and frequency with bus Close main breaker when generators are in phase Turn off synchroscope |
|
Adjust load on incoming generator |
Transfer voltage regulator to automatic Balance active (kw) load Balance reactive (kvar) Load |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Operate electrical, electronic and control systems |
B1.1 Basic configuration and operation principles of the following electrical equipment:
|
Parallel generators |

Assessment OICEW-8-1A
Lathe project
Assessed in EN-2112 Machine Tool Technology
Condition
In workshop, given access to a lathe, mild steel rod stock and other necessary equipment and supplies.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Plan and Use the lathe to produce a project in accordance with attached drawing |
|
Attachment:
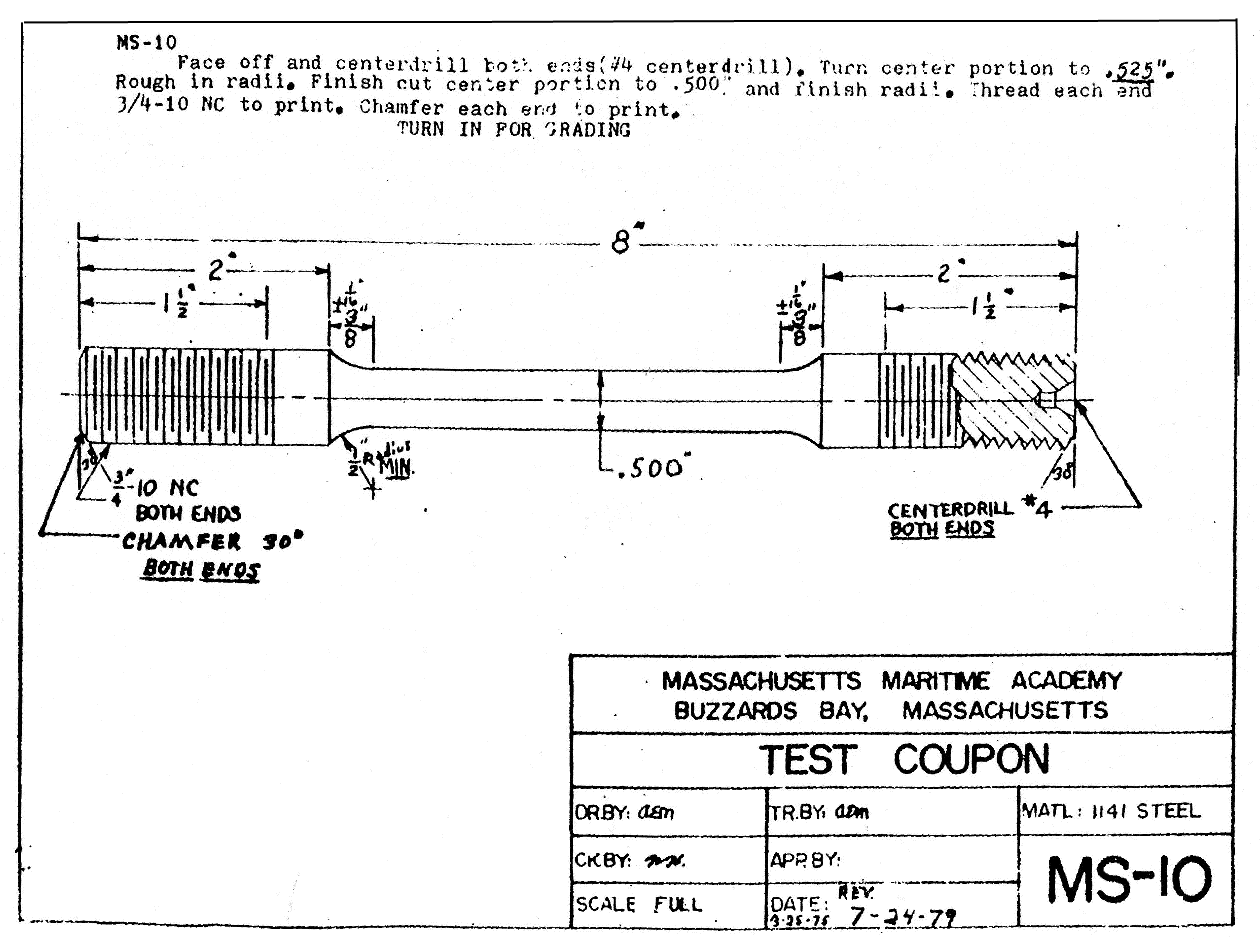
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Appropriate use of hand tools, machine tools and measuring instruments for fabrication and repair on board |
C1.6 Use of hand tools, machine tools and measuring instruments |
Lathe project |

Assessment OICEW-8-2A
Centrifugal pump maintenance
Assessed in EN-2111 Auxiliary Machinery II
Condition
Aboard ship or in workshop, given a centrifugal pump and other equipment, manuals and specifications needed to complete the task.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Disassemble centrifugal pump | |
|
Inspect all parts for wear and deterioration |
Check the following:
|
|
Repair centrifugal pump |
Replace parts as necessary to bring pump to manufacturers specifications |
|
Reassemble centrifugal pump |
Replace and adjust seals/gaskets as necessary |
|
Test centrifugal pump |
Operate under load and inspect for abnormalities |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Maintenance and repair of shipboard machinery and equipment |
C2.3 Maintenance and repair, such as dismantling, adjustment and reassembling of machinery and equipment |
Centrifugal pump maintenance |

Assessment OICEW-8-2B
Reciprocating pump maintenance
Assessed in EN-2111 Auxiliary Machinery II
Condition
Aboard ship or in workshop, given a reciprocating pump and other equipment, manuals and specifications needed to complete the task.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Disassemble reciprocating pump | |
|
Inspect all parts for wear and deterioration |
Check the following:
|
|
Repair reciprocating pump |
Replace parts as necessary to bring pump to manufacturers specifications |
|
Reassemble reciprocating pump |
Replace and adjust seals/gaskets as necessary Adjust valve tappets for proper operation |
|
Test reciprocating pump |
Operate under load and inspect for abnormalities |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Maintenance and repair of shipboard machinery and equipment |
C2.3 Maintenance and repair, such as dismantling, adjustment and reassembling of machinery and equipment |
Reciprocating pump maintenance |

Assessment OICEW-8-2C
Gear pump maintenance
Assessed in EN-2231 Sea Term II: Marine Engineering
Condition
Aboard ship or in workshop, given a gear pump and other equipment, manuals and specifications needed to complete the task.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Disassemble gear pump | |
|
Inspect all parts for wear and deterioration |
Check the following clearances:
|
|
Repair gear pump |
Replace parts as necessary to bring pump to manufacturers specifications |
|
Reassemble gear pump |
Replace and adjust seals/gaskets as necessary |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Maintenance and repair of shipboard machinery and equipment |
C2.3 Maintenance and repair, such as dismantling, adjustment and reassembling of machinery and equipment |
Gear pump maintenance |

Assessment OICEW-8-2D
Inspect valve manifold
Assessed in EN-2231 Sea Term II: Marine Engineering
Condition
Aboard ship or in workshop, given a piping diagram and other equipment needed to complete the task.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Lockout/tagout valve manifold |
Identify contents of pipe Isolate pipe section Relieve pressure and drain section |
|
Use tools to open up piping for inspection |
Use:
|
|
Dismantle flanges Inspect interior of pipe Clean and prepare joints for reassembly | |
|
Use tools and proper joint materials to close up piping system |
Use:
|
|
Test system to identify leaks |
Perform hydrostatic test for leakage Prove joint leak free |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Maintenance and repair of shipboard machinery and equipment |
C2.3 Maintenance and repair, such as dismantling, adjustment and reassembling of machinery and equipment |
Inspect valve manifold |

Assessment OICEW-8-2E
Overhaul valve
Assessed in EN-2231 Sea Term II: Marine Engineering
Condition
Aboard ship or in workshop, given one of the following types of valves: safety valve, steam trap, quick closing valve, drain valve or relief valve, and other equipment needed to complete the task.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Disassemble a globe valve |
Remove old packing from stuffing box |
|
Inspect valve |
Examine disk and seat Blue-in valve disk and seat |
|
Repair valve as necessary |
Machine, grind-in and bed-in valve disk and seat as required Replace bonnet gasket Select and install new packing |
|
Reassemble valve |
Prove valve leak free with hydrostatic test |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Maintenance and repair of shipboard machinery and equipment |
C2.3 Maintenance and repair, such as dismantling, adjustment and reassembling of machinery and equipment |
Overhaul valve |

Assessment OICEW-8-2F
Overhaul heat exchanger
Assessed in EN-2231 Sea Term II: Marine Engineering
Condition
Aboard ship or in workshop, given a heat exchanger and other equipment needed to complete the task.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Disassemble heat exchanger | |
|
Inspect heat exchanger |
Perform hydrostatic test or black light/dye test for tube and seal leakage Note indications of corrosion, erosion, and fouling |
|
Maintain heat exchanger |
As necessary:
|
|
Reassemble heat exchanger |
Fill and prove leak free |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Maintenance and repair of shipboard machinery and equipment |
C2.3 Maintenance and repair, such as dismantling, adjustment and reassembling of machinery and equipment |
Overhaul heat exchanger |

Assessment OICEW-8-2G
Routine Maintenance feed pump lube oil system
Assessed in EN-2231 Sea Term II: Marine Engineering
Condition
Aboard ship or in workshop, given access to s feed pump and other equipment needed to complete the task.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Identify and describe:
| |
|
Check feed pump oil level |
State type and location of replenishment oil Add oil, if required |
|
Check for adequate coolant flow |
Feel coolant line Clean strainer, if required |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Maintenance and repair of shipboard machinery and equipment |
C2.3 Maintenance and repair, such as dismantling, adjustment and reassembling of machinery and equipment |
Routine Maintenance feed pump lube oil system |

Assessment OICEW-8-2H
Routine maintenance compressed air system
Assessed in EN-2231 Sea Term II: Marine Engineering
Condition
Aboard ship or in workshop, given access to a compressed air system and other equipment needed to complete the task.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Check operating air compressors |
Check operating pressure Check compressor lubrication Add oil, if required Check belts, if installed Check operation of pressure switch, if installed |
|
Blow down sufficiently to remove accumulated moisture Check receiver pressure | |
|
Blow down, as necessary |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Maintenance and repair of shipboard machinery and equipment |
C2.3 Maintenance and repair, such as dismantling, adjustment and reassembling of machinery and equipment |
Routine maintenance compressed air system |

Assessment OICEW-9-1A
Monitor sanitary flushing water system
Assessed in EN-2231 Sea Term II: Marine Engineering
Condition
Aboard ship or in an approved simulator, given access to a sanitary flushing water system and proper tools and equipment.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Identify the source of flushing water |
Identify operating sanitary pump Identify alternate sources |
|
Describe the operation of the hydro-pneumatic tank |
State purpose of air cushion State corrective action for short cycling |
|
Monitor the sanitary pump |
Check operating pressure Check motors for overheating/vibrations Check strainer pressure differential |
|
Monitor the hydro-pneumatic tank |
Note cut-in and cut-out pressures |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Ensure compliance with pollution- prevention requirements |
D1.2 Anti-pollution procedures and all associated equipment |
Monitor sanitary flushing water system |

Assessment OICEW-9-1B
Monitor sewage waste treatment plant
Assessed in EN-2231 Sea Term II: Marine Engineering
Condition
Aboard ship or in an approved simulator, given access to a sewage waste treatment plant and proper tools and equipment.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Identify and Describe the visible components of the msd and lift station |
Identify and describe at least the following:
|
|
Trace the discharge piping of the msd. |
Trace system in auxiliary machinery room only |
|
Monitor the msd. |
Monitor for at least one hour Maintain log Add chemicals as required |
|
Apply regulations to the operation of the MSD |
State requirements for overboard discharge of waste |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Ensure compliance with pollution- prevention requirements |
D1.2 Anti-pollution procedures and all associated equipment |
Monitor sewage waste treatment plant |

Assessment OICEW-9-1C
Monitor oily water separator system
Assessed in EN-2231 Sea Term II: Marine Engineering
Condition
Aboard ship or in an approved simulator, given access to an oily water separator system and proper tools and equipment.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Identify and describe at least the following:
| |
|
Trace the suction and discharge of the OWS. |
Trace system for current operating condition |
|
Monitor the OWS. |
Monitor OWS for at least one hour Check bilge level Maintain OWS log |
|
Apply regulations to the operation of the OWS |
Know permissible oil content for discharge Fill out sample Oil Record Book |
Supports Table A-III/1 officers in charge of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Operate fuel, lubrication, ballast and other pumping systems and associated control systems |
A5.3 Oily-water separators (or-similar equipment) requirements and operation |
Monitor oily water separator system |

Assessment RFPEW-5-2E
Change Burner
Assessed in EN-2231 Sea Term II: Marine Engineering
Condition
Aboard a ship, in port or underway, or in an approved simulator or laboratory, given proper equipment.
Performance Requirements
| Behavior | Standard |
|---|---|
| The student will: | During assessment, the student shall, at a minimum: |
|
Identify and Describe components of boiler burner and register |
Identify:
|
|
Change Over burner |
Determine which burner will be taken out of service Determine which burner will be lit off Insure availability of steam atomization and fuel oil Insert clean burner Line up fuel and steam atomization Light off clean burner Secure dirty burner Remove dirty burner and drain burner of residual fuel oil |
|
Steam clean dirty burner Disassemble and clean burner parts as necessary Inspect nozzle tips Reassemble burner |
Supports Table A-III/4 ratings forming part of an engineering watch
| Competence | Knowledge, Understanding & Proficiency | Task |
|---|---|---|
|
For keeping a boiler watch: Maintain the correct water levels and steam pressures |
A2.1 Safe operation of boilers |
Change Burner |